You turn on your air purifier and trust it’s doing something. But what’s really happening inside that plastic box? And are you paying for technology that actually works, or just fancy marketing?
Let’s break down how each type of air purifier filter works so you know exactly what you’re buying.
The 3 Main Types of Air Purifier Filters
Most quality air purifiers use a combination of three filter types:
1. Pre-filters (catch the big stuff)
2. HEPA filters (trap microscopic particles)
3. Activated carbon filters (absorb odors and gases)
Some models add extra tech like UV-C lights or ionizers. We’ll cover all of it.
🧪 How HEPA Filters Work (The Science Part)
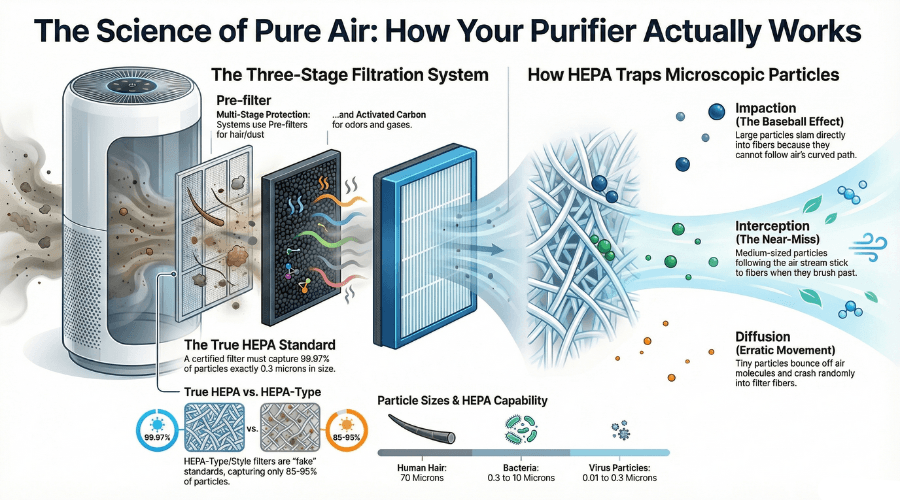
HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air. A True HEPA filter must capture 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns.
For context:
– Human hair: 70 microns
– Pollen: 10-100 microns
– Dust mite waste: 10-40 microns
– Bacteria: 0.3-10 microns
– Virus particles: 0.01-0.3 microns
The Capture Methods
HEPA filters don’t work like a simple screen. They trap particles using three different mechanisms:
1. Interception
Particles follow the air stream. When they come within one radius of a fiber, they stick to it. This works for medium-sized particles.
2. Impaction
Larger particles can’t follow the air’s curved path around fibers. They slam into the fiber and stick. Think of it like throwing a baseball at a net.
3. Diffusion
Tiny particles (under 0.1 microns) move erratically due to air molecules bumping them around. This random movement eventually leads them to crash into a fiber.
The weird thing? HEPA filters are MOST efficient at capturing particles smaller and larger than 0.3 microns. The 0.3-micron size is actually the hardest to trap, which is why it’s the testing standard.
True HEPA vs HEPA-Type: Know the Difference
Watch out for these marketing terms:
– True HEPA / Medical-Grade HEPA: Meets the 99.97% standard
– HEPA-Type / HEPA-Like / HEPA-Style: Fake. Usually only captures 85-95% of particles
Don’t buy “HEPA-type” filters if you have allergies or asthma. They’re not the same thing.
🔵 How UV-C Light Purification Works
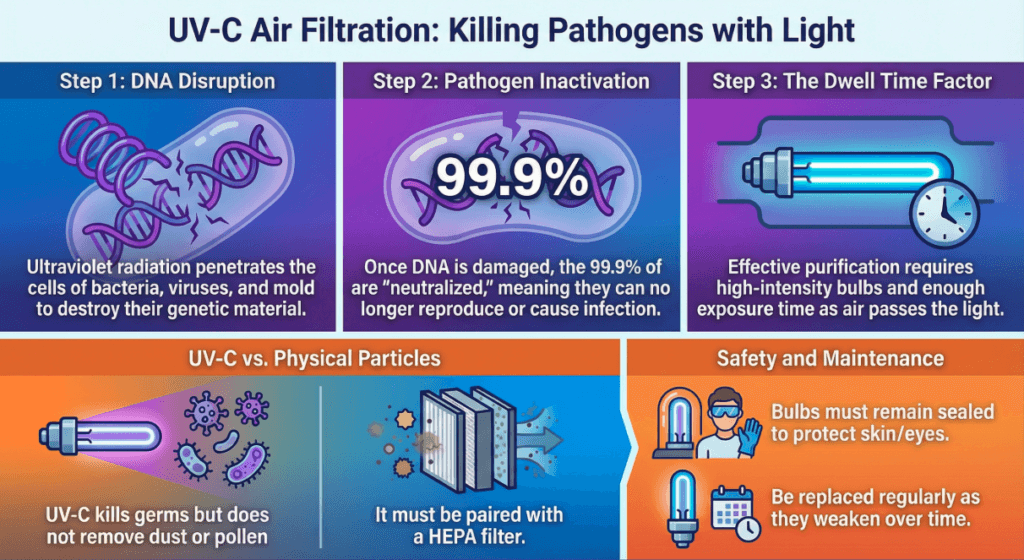
UV-C light uses ultraviolet radiation to damage the DNA of bacteria, viruses, and mold spores.
Does It Actually Work?
Yes, but with big caveats.
Lab tests show UV-C kills 99.9% of airborne pathogens when exposed long enough. The problem is “long enough.” In most air purifiers, particles zoom past the UV-C bulb in fractions of a second.
For UV-C to work well, you need:
– High-intensity bulbs
– Longer exposure time
– Regular bulb replacement (they weaken over time)
What UV-C Can’t Do
UV-C light does NOT remove particles from the air. It doesn’t touch dust, pollen, or allergens. You still need a HEPA filter.
Think of UV-C as a bonus feature, not a replacement for mechanical filtration.
Safety Concerns
Quality air purifiers keep UV-C bulbs sealed inside. You never see the light directly. Direct exposure to UV-C radiation damages skin and eyes, so never bypass safety features.
⚫ How Activated Carbon Filters Work
Carbon filters handle what HEPA can’t: gases, odors, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
The Adsorption Process
Notice I said “adsorption,” not “absorption.” That’s not a typo.
Adsorption means molecules stick to the surface of the carbon. Activated carbon is incredibly porous. One gram has a surface area of 500-3,000 square meters (that’s up to 7 basketball courts).
Gas molecules and odor compounds get trapped in millions of tiny pores. They stick through weak chemical bonds.
What Carbon Removes
✅ Cooking odors
✅ Pet smells
✅ Smoke (including cigarette smoke)
✅ VOCs from paint, cleaning products, furniture
✅ Formaldehyde
✅ Benzene
What Carbon Can’t Remove
❌ Particles (you need HEPA for that)
❌ High concentrations of chemicals (it saturates quickly)
❌ Carbon monoxide or radon (different filtration needed)
Carbon Filter Lifespan
Here’s the catch: once carbon pores fill up, the filter stops working. Unlike HEPA filters that you can see getting dirty, carbon filters fail invisibly.
Replace carbon filters every 3-6 months depending on:
– Air quality in your home
– How often you run the purifier
– How much carbon the filter contains (more is better)
🌀 Pre-Filters: The Unsung Heroes
Pre-filters are the first line of defense. They catch large particles like:
– Pet hair
– Lint
– Dust bunnies
– Visible debris
Most pre-filters are washable and reusable. Clean them every 2-4 weeks to prevent your HEPA filter from clogging prematurely.
A clogged pre-filter reduces airflow and makes your entire system work harder. Clean filters = better performance + lower electricity costs.
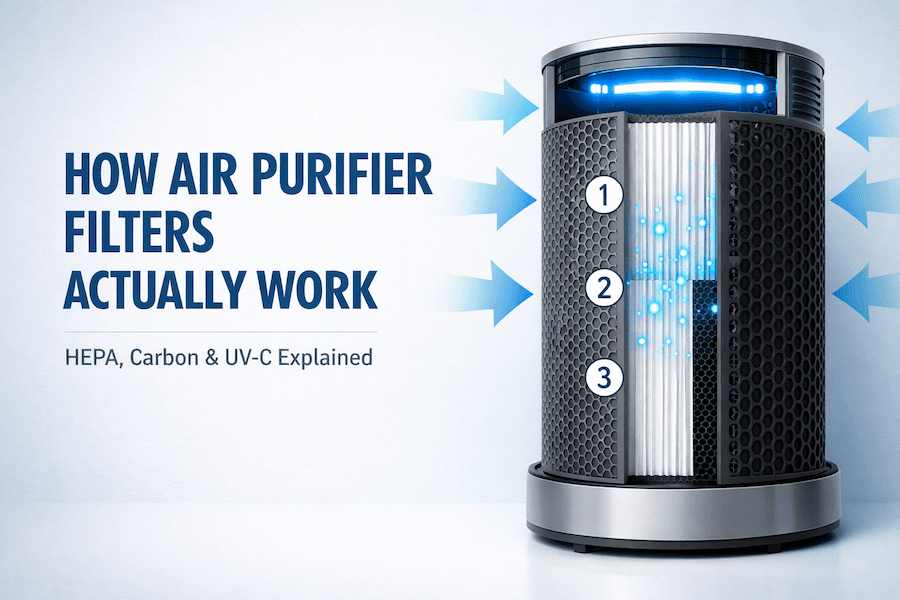
🔄 How Complete Filtration Systems Work Together
Quality air purifiers use multiple filters in sequence:
Step 1: Pre-Filter
Catches hair, lint, and large dust particles
Step 2: Activated Carbon
Absorbs gases, odors, and chemical vapors
Step 3: HEPA Filter
Traps microscopic particles and allergens
Step 4: UV-C Light (optional)
Kills bacteria, viruses, and mold spores
Air flows through each stage. By the end, you’ve removed particles, neutralized odors, and killed germs.
📊 Do Air Purifier Filters Lose Effectiveness Over Time?
Yes, absolutely.
HEPA Filters
As particles accumulate, airflow resistance increases. Your purifier has to work harder to push air through. Eventually, the motor can’t overcome the resistance, and cleaning efficiency drops.
Most HEPA filters last 6-12 months. Replace them when:
– Airflow noticeably decreases
– The filter looks visibly gray or black
– Your purifier’s filter indicator lights up
Carbon Filters
Carbon saturates faster than HEPA. Once the pores fill, the filter does nothing for odors.
Replace carbon filters every 3-6 months, especially if you:
– Have pets
– Cook frequently
– Live in a city with poor air quality
– Recently painted or renovated
UV-C Bulbs
UV-C intensity decreases over time. Most bulbs need replacement every 10-12 months, even if they still light up. Lower intensity = less effective germicidal action.
💡 Common Filter Questions Answered
Can you wash HEPA filters to reuse them?
No. Water destroys the fiber structure. Some manufacturers sell “washable HEPA” filters, but they typically don’t meet True HEPA standards and have lower efficiency.
Do you need both HEPA and carbon filters?
If you want to remove both particles AND odors, yes. HEPA handles particles, carbon handles gases. Neither does what the other does.
How often should you run your air purifier?
For best results, run it 24/7 on auto or medium speed. Air quality degrades quickly when the purifier stops. Continuous operation provides consistent clean air.
Do filters need a “break-in” period?
No. Filters work at full efficiency immediately. Any smell when you first turn on a new filter is residual manufacturing odors, not a sign it needs breaking in.
🔗 Want to Learn More?
Check out these related guides:
– GermGuardian AC3200 Review: Complete Buyer’s Guide
– Understanding Air Purifier Coverage: Room Size vs ACH
– Complete Air Purifier Maintenance Schedule
– 12 Common Air Purifier Problems and Fixes
The Bottom Line
Air purifier filters aren’t magic, they’re applied physics and chemistry. HEPA filters trap particles mechanically, carbon filters adsorb gases chemically, and UV-C light damages microorganism DNA.
When you understand how each filter type works, you can make smarter buying decisions and maintain your system properly.
Don’t fall for marketing gimmicks. Focus on proven technologies: True HEPA for particles, activated carbon for odors, and UV-C as an optional bonus.










Recent Comments